Git command share and CI/CD introduction
Git introduction
- Git is a distributed version control concept, comparing with traditional version control like subversion, it has some advantages:
- Local repository
- More efficient
- Better collaboration abilities
- Non-linearly workflow, continuous integration
- Git also has some disadvantage from what I think:
- More steep learning curve
- Local saved files may be easily lost than keep in centralised server
- Illegal operation may cause problem for others to collaboration
Git command share
Custom commit template
- Create a template file
- ~/.gitmessage.txt
: subject
[why]
#describe your question
[how]
#describe your solution
JIRA:
- Setup git configuration
- $ git config –global commit.template ~/.gitmessage.txt
Amend a Commit
-
Stage all changes and amend
- $ git commit -a –amend
-
Stage specified changes and commit
-
$ git add/rm/reset -p
-
git commit –amend
-
-
Note: amended commit has different commit-id
Advanced Git Log
-
Author, committer ma be different
- after “git cherry-pick”, “git rebase” operation
-
To display committer information
- $ git log/show –pretty=fuller
-
To reset author information
- $ git commit –amend –reset-author
-
Related Gerrit access control
- Forge Author/Committer Identity
List Branch
-
List available branches
- $ git branch [-r/-a]
-
Local branch files
- $ tree .git/refs
Sort Branch
-
Sort branch by committer date
- $ git branch -r –sort committerdate
-
Usage
- compare local & remote branches (remember git-fetch first to update)
- compare branches of multiple remote repositories
Tag
-
Tag is read-only commit reference
- .git/refs/tags/
- .git/refs/tags/
-
Add light-weight tag
- $git tag
[commit]
- $git tag
-
Add annotate/signed tag
- $ git tag -a/-s
[commit]
- $ git tag -a/-s
-
Delete tag
- local: $ git tag -d
- remote: $ git put
:refs/tags/
- local: $ git tag -d
Note
-
Add or inspect notes to commits
- usage: Gerrit review, Jenkins job, personal note
- .git/refs/notes/
-
Add/remove a note
- $ git notes [–ref
] add/remove [commit] - default note-ref: commits
- $ git notes [–ref
-
Display commit notes (with commit log)
- $ git log –show-notes=
- $ git log –show-notes=
-
Git doesn’t fetch remote notes by default
- $ git fetch origin refs/notes/:refs/notes/
-
Add personal note example
- git notes add -m “Check this commit later” HEAD
- git log
Remote Repository
-
Add a remote repository
- $ git remote add
- $ git remote add
-
Fetch remote repository
- $ git fetch
- $ git fetch
-
Create/Push remote reference
- $ git push
[-f] :
- $ git push
-
Delete remote reference
- $ git push
:
- $ git push
Git for Software Version
-
Git-describe
- $ git describe
-
Get a sequential number
- Count commit number
- $ git rev-list HEAD | wc -l
- Trap
- different branches may have same commit numbers
- need to disable clone-depth in case not complete history
- Count commit number
Gerrit introduction
-
Gerrit is a free & web-based team code collaboration tool
- Original author: Google (for Android)
- https://www.gerritcodereview.com
-
Major feature
- central git repositories
- code review & discuss
- easy Henkins integration
Gerrit architecture
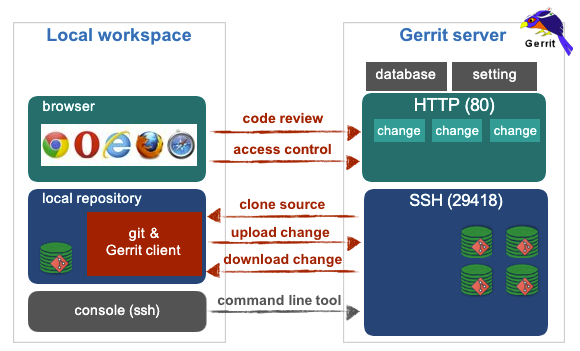
Gerrit user configuration
SSH Configuration
- Generate ssh rsa key pair for Gerrit git repositories
ssh-keygen
-Edit .ssh/config to specify user & private key
User Configuration
- Sign-in Gerrit server through http -> Setting
Gerrit + Jenkins Workflow
- Jenkins: continuous integrating changes
- auto build, analysis, test: verify +-1
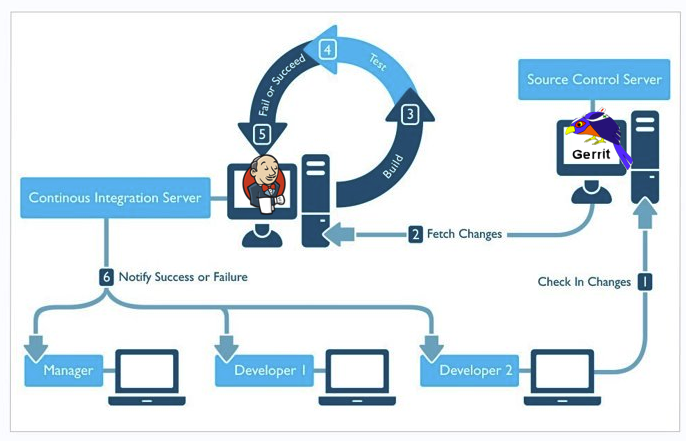
Gerrit Roles definition
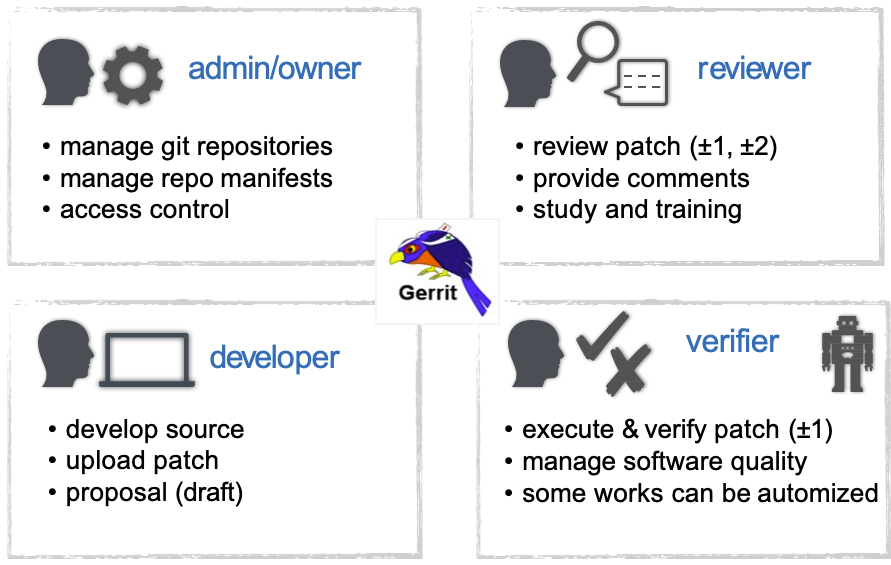
Summary
- Gerrit - a key component for SDLC
- for efficient software development
- central Git repositories with access control
- for better software quality
- code review & discuss
- Jenkins integration (auto test/analysis)
- for efficient software development